The Importance of Exercising During Pregnancy
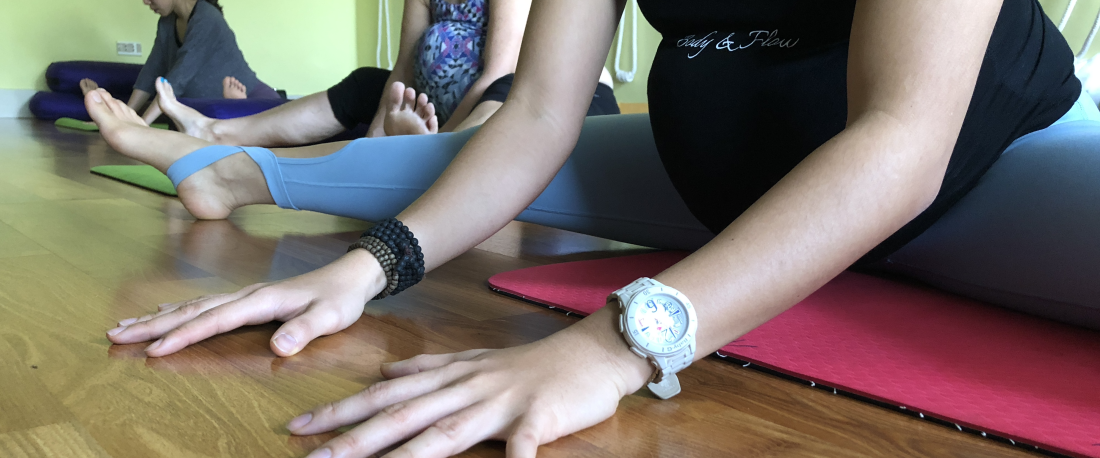
Pregnancy is a transformative time in a woman’s life, marked by joy, anticipation, and sometimes, a few discomforts. Among the many decisions expectant mothers make, one of the most important is whether to incorporate exercise into their routine during these nine months. The answer, supported by a growing body of research and endorsed by healthcare professionals, is a resounding “yes.” Exercising during pregnancy is not just safe; it’s also a pivotal step toward ensuring a healthier journey for both the mother and her baby.
1. Reducing the Risk of Gestational Diabetes:
A study published in the journal Obstetrics and Gynecology in 2017 found that women who engaged in regular exercise during pregnancy had a significantly lower risk of developing gestational diabetes compared to those who did not exercise. The research highlights the role of exercise in mitigating this common pregnancy complication and its potential long-term health benefits for both the mother and the baby.
Source: Retnakaran, R., et al. (2017). Effect of Prenatal Exercise on Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstetrics & Gynecology, 129(6), 1081-1088.
2. Improved Mood and Reduced Anxiety:
Research published in the journal Sports Medicine in 2018 suggests that exercise during pregnancy can have a positive impact on mental health. Regular physical activity has been shown to increase the release of endorphins, which can help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression often experienced during pregnancy.
Source: Daley, A. J., et al. (2018). The Effects of Exercise on Mental Health during Pregnancy: A Systematic Review. Sports Medicine, 48(2), 198-208.
3. Managing Weight Gain:
A study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology in 2018 found that women who engaged in moderate-intensity exercise during pregnancy were less likely to gain excess weight compared to those who were sedentary. Controlling excessive weight gain during pregnancy can reduce the risk of complications such as gestational diabetes and high blood pressure.
Source: Mottola, M. F., et al. (2018). 2019 Canadian guideline for physical activity throughout pregnancy. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 221(6), 644-651.
4. Enhanced Sleep Quality:
A study in the journal Sleep Medicine in 2017 examined the effects of exercise on sleep quality during pregnancy. The findings suggested that regular exercise was associated with improved sleep patterns, reduced insomnia, and better overall sleep quality among pregnant women.
Source: Reid, K. J., et al. (2017). Exercise during pregnancy: Sleep quality and sleep disturbances. Sleep Medicine, 38, 100-107.
5. Preparing for Labor and Delivery:
Research published in the Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology in 2015 indicated that regular exercise during pregnancy can improve maternal fitness, increase strength, and enhance overall physical readiness for labor and delivery.
Source: Petrov Fieril, K., et al. (2015). The benefits of aerobic exercise in patients with sub-acute stroke. Stroke Research and Treatment, 2015.
These research findings underscore the numerous benefits of exercising during pregnancy, including reducing the risk of complications, enhancing mental well-being, managing weight gain, improving sleep quality, and preparing the body for the demands of labor and delivery. However, it’s crucial to note that each pregnancy is unique, and exercise recommendations should be tailored to individual circumstances and always conducted under professional guidance.